Newton’s First Law (Law of Inertia): An object remains at rest or in uniform motion unless acted upon by an external force
Newton’s Second Law (Law of Motion): Force is proportional to the mass of an object and its acceleration (F = ma).
Newton’s Third Law (Action and Reaction): For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
James Webb Space Telescope
Peering into the cosmos with unprecedented clarity, the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) offers an infrared glimpse into the universe’s distant past. These slides show JWST vs. Hubble Space Telescope.
Physics and Space Science

Earth Science & History
Chemistry & Materials Sciences
- Aristotle (384–322 BC)
- Archimedes (c. 287–212 BC)
- Alhazen (965–1040)
- Copernicus (1473–1543)
- Galileo (1564–1642)
- Johannes Kepler (1571–1630)
- Isaac Newton (1643–1727)
- Carl Linnaeus (1707–1778)
- Antoine Lavoisier (1743–1794)
- Michael Faraday (1791–1867)
- Charles Darwin (1809–1882)
- Gregor Mendel (1822–1884)
- Marie Curie (1867–1934)
- Max Planck (1858–1947)
- Albert Einstein (1879–1955)
- Niels Bohr (1885–1962)
- Ernest O. Lawrence (1901–1958)
- Erwin Schrödinger (1887–1961)
- Linus Pauling (1901–1994)
- Barbara McClintock (1902–1992)
- Richard Feynman (1918–1988)
- Watson and Crick (1916–2004)
- Rosalind Franklin (1920–1958)
- Stephen Hawking (1942–2018)
- Tim Berners-Lee (born 1955)
-

Aristotle
Aristotle (384–322 BC)Aristotle (384–322 BC): Aristotle was a leading figure in the history of ancient philosophy and science. Born in Northern Greece, he was a philosopher and genius during the Classical period. As a student of Plato and the teacher of Alexander the Great, he was part of an intellectual lineage that profoundly influenced the Western intellectual tradition. Aristotle’s impact on philosophy and various sciences cannot be overstated. His inquiries spanned a multitude of subjects, including physics, biology, zoology, metaphysics, logic, ethics, aesthetics, poetry, theater, music, rhetoric, psychology, and politics. In the realm of physical science, his meticulous observations and powerful theorizations formed the basis for subsequent scientific exploration.
Aristotle
Aristotle (384–322 BC): Aristotle was a leading figure in the history of ancient philosophy and science. Born in Northern Greece, he was a philosopher and genius during the Classical period. As a student of Plato and the teacher of Alexander the Great, he was part of an intellectual lineage that profoundly influenced the Western intellectual […] -

Archimedes
Archimedes (c. 287–212 BC)Archimedes (c. 287–212 BC): Archimedes was an Ancient Greek mathematician, physicist, engineer, inventor, and astronomer whose contributions were significant in the development of the foundations of mathematics and science. His vast intellect and knack for problem-solving made him one of the most influential figures in the scientific world. Archimedes formulated concepts including the principles of leverage and buoyancy which are still widely used in modern physics and engineering. He also invented practical devices including the screw pump that bears his name – the Archimedean screw. Archimedes also made advancements in the field of mathematics with the estimate of pi and the method of exhaustion which is a precursor to integral calculus.
Archimedes
Archimedes (c. 287–212 BC): Archimedes was an Ancient Greek mathematician, physicist, engineer, inventor, and astronomer whose contributions were significant in the development of the foundations of mathematics and science. His vast intellect and knack for problem-solving made him one of the most influential figures in the scientific world. Archimedes formulated concepts including the principles of […] -

Alhazen
Alhazen (965–1040)Alhazen (Ibn al-Haytham) (965–1040): Alhazen was a renowned Arab mathematician, astronomer, and physicist, known for his contributions to the principles of optics and visual perception. His work in the field of optics shifted the understanding of light and vision. He is considered the father of modern optics. Alhazen introduced the concept of analyzing light through the use of a pinhole camera and was also the first to understand that vision occurs when light bounces off an object and then is directed to one’s eyes. Alhazen’s meticulous approach to understanding and explaining scientific phenomena using observation, hypothesis, and experimental verification laid the groundwork for the modern scientific method.
Alhazen
Alhazen (Ibn al-Haytham) (965–1040): Alhazen was a renowned Arab mathematician, astronomer, and physicist, known for his contributions to the principles of optics and visual perception. His work in the field of optics shifted the understanding of light and vision. He is considered the father of modern optics. Alhazen introduced the concept of analyzing light through […] -

Copernicus
Copernicus (1473–1543)Nicolaus Copernicus (1473–1543): Nicolaus Copernicus revolutionized our understanding of the cosmos. Known primarily for formulating a heliocentric cosmology, Copernicus’ model displaced the Earth from the center of the universe and positioned the Sun at the heart of the solar system. Although controversial in his time, this perspective provided the foundation for the future development of modern astronomy, changing the course of scientific thought forever.
Copernicus
Nicolaus Copernicus (1473–1543): Nicolaus Copernicus revolutionized our understanding of the cosmos. Known primarily for formulating a heliocentric cosmology, Copernicus’ model displaced the Earth from the center of the universe and positioned the Sun at the heart of the solar system. Although controversial in his time, this perspective provided the foundation for the future development of […] -

Galileo
Galileo (1564–1642)Galileo Galilei (1564–1642): Galileo is often regarded as the “father of observational astronomy,” and was a important figure in the Scientific Revolution. He made significant improvements to the telescope and subsequently made critical astronomical observations that supported Copernican concepts. Galileo’s observations of inertia and the laws of motion laid the groundwork for the principles of classical physics. Galileo’s work spanned a variety of fields, including physics, engineering, and natural philosophy, and his contributions have had a foundational impact on the trajectory of scientific discovery.
Galileo
Galileo Galilei (1564–1642): Galileo is often regarded as the “father of observational astronomy,” and was a important figure in the Scientific Revolution. He made significant improvements to the telescope and subsequently made critical astronomical observations that supported Copernican concepts. Galileo’s observations of inertia and the laws of motion laid the groundwork for the principles of […] -

Johannes Kepler
Johannes Kepler (1571–1630)Johannes Kepler (1571–1630): Johannes Kepler was a German astronomer, mathematician, and astrologer whose innovative work transformed our understanding of the cosmos. Kepler formulated three major laws of planetary motion which corrected and refined the previous heliocentric model proposed by Nicolaus Copernicus. His laws accurately described the elliptical orbits of planets around the sun and the relationship between a planet’s orbital speed and its distance from the sun. Giving us the precise correlation between the orbital periods of any two planets. These laws provided a powerful model for planetary motion and formed a vital link in the chain of scientific understanding that led to the formulation of Newton’s law of universal gravitation.
Johannes Kepler
Johannes Kepler (1571–1630): Johannes Kepler was a German astronomer, mathematician, and astrologer whose innovative work transformed our understanding of the cosmos. Kepler formulated three major laws of planetary motion which corrected and refined the previous heliocentric model proposed by Nicolaus Copernicus. His laws accurately described the elliptical orbits of planets around the sun and the […] -

Isaac Newton
Isaac Newton (1643–1727)Isaac Newton (1643–1727): Isaac Newton was a significant figure in the scientific revolution of the 17th century. Born in England, he was a mathematician, physicist, and astronomer who is best known for formulating the laws of motion and universal gravitation. Newton’s three laws of motion describe the relationship between a body and the forces acting upon it and its motion in response to those forces. These laws laid the groundwork for classical mechanics. The law of universal gravitation described the fundamental force of attraction that exists between any two masses. His ideas continue to influence our understanding of the physical universe. Newton’s insights marked a new era in scientific theory while shifting the course of physics from a descriptive to a predictive discipline.
Isaac Newton
Isaac Newton (1643–1727): Isaac Newton was a significant figure in the scientific revolution of the 17th century. Born in England, he was a mathematician, physicist, and astronomer who is best known for formulating the laws of motion and universal gravitation. Newton’s three laws of motion describe the relationship between a body and the forces acting […] -

Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (1707–1778)Carl Linnaeus (1707–1778): Carl Linnaeus was a Swedish botanist, physician, and zoologist who established the modern system of naming organisms known as binomial nomenclature. Born in the early 18th century, Linnaeus is often referred to as the “father of modern taxonomy” for his contributions to the field. He developed a system for classifying and naming species based on shared characteristics. This method that is still in use today. His ordered system of classification in which species are grouped into broader categories of genus, family, order, class, phylum, and kingdom, provided an essential framework for the study of biology.
Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (1707–1778): Carl Linnaeus was a Swedish botanist, physician, and zoologist who established the modern system of naming organisms known as binomial nomenclature. Born in the early 18th century, Linnaeus is often referred to as the “father of modern taxonomy” for his contributions to the field. He developed a system for classifying and naming […] -

Antoine Lavoisier
Antoine Lavoisier (1743–1794)Antoine Lavoisier (1743–1794): Antoine Lavoisier was a prominent French chemist renowned for his significant contributions that reshaped the field of chemistry in the late 18th century. He developed the theory of conservation of mass which states that the mass of a closed system will remain constant regardless of the processes acting inside the system. This revolutionary concept led to the law of conservation of matter in chemical reactions. Lavoisier also identified and named two fundamental chemical elements: oxygen and hydrogen. His experiments led him to propose that combustion and respiration are caused by chemical reactions with oxygen, effectively debunking the long-standing phlogiston theory. Due to his work, Lavoisier is often referred to as the “father of modern chemistry.” His rigorous methods, insistence on precise measurement and clear definitions significantly elevated the scientific approach in chemistry.
Antoine Lavoisier
Antoine Lavoisier (1743–1794): Antoine Lavoisier was a prominent French chemist renowned for his significant contributions that reshaped the field of chemistry in the late 18th century. He developed the theory of conservation of mass which states that the mass of a closed system will remain constant regardless of the processes acting inside the system. This […] -

Michael Faraday
Michael Faraday (1791–1867)Michael Faraday (1791–1867): Michael Faraday was a British scientist known for his significant contributions to the fields of electromagnetism and electrochemistry. Born to a poor family in the late 18th century, Faraday received minimal education but his scientific curiosity led him to become one of the most influential scientists in history. His main discoveries include the principles of electromagnetic induction, diamagnetism, and electrolysis. Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction, which states that a change in the magnetic field within a closed loop of wire induces an electromotive force in the wire, is a fundamental principle used in modern electric power generation and transmission. His work on diamagnetism was a pioneering endeavor in the field. His laws of electrolysis serve as the basis for electrochemistry, which has numerous applications in batteries and fuel cells. Faraday’s contributions have had enduring impact on our technological world, including electric motor technology and telecommunications.
Michael Faraday
Michael Faraday (1791–1867): Michael Faraday was a British scientist known for his significant contributions to the fields of electromagnetism and electrochemistry. Born to a poor family in the late 18th century, Faraday received minimal education but his scientific curiosity led him to become one of the most influential scientists in history. His main discoveries include […] -

Charles Darwin
Charles Darwin (1809–1882)Charles Darwin (1809–1882): Charles Darwin was a renowned British naturalist and biologist who fundamentally changed the way we understand the natural world. Born in the early 19th century, Darwin formulated the theory of natural selection, a revolutionary concept that explains how species evolve over time through gradual changes. Darwin argued that individuals within a species show variation in their traits and those with traits better suited to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce. Over generations, these important traits become more common within the population leading to evolutionary change. This idea was presented in his book, “On the Origin of Species,” which shook the scientific world and caused a paradigm shift in our understanding of life on Earth. Darwin laid the groundwork for the modern science of biology, making him one of the most influential figures in human history.
Charles Darwin
Charles Darwin (1809–1882): Charles Darwin was a renowned British naturalist and biologist who fundamentally changed the way we understand the natural world. Born in the early 19th century, Darwin formulated the theory of natural selection, a revolutionary concept that explains how species evolve over time through gradual changes. Darwin argued that individuals within a species […] -

Gregor Mendel
Gregor Mendel (1822–1884)Gregor Mendel (1822–1884): Gregor Mendel was an Augustinian monk and botanist whose experiments in breeding garden peas led to the establishment of the fundamental laws of genetics. Born in the early 19th century in what is now the Czech Republic, Mendel’s meticulous work with pea plants laid the foundation for the field of genetics. He demonstrated that the inheritance of certain traits in the plants follows particular patterns now referred to as the laws of Mendelian inheritance. His most significant contributions include the Law of Segregation which states that an individual inherits one allele from each parent for each trait. His Law of Independent Assortment pose that traits are passed independently of one another from parents to offspring. Mendel’s work was largely unrecognized during his lifetime but was rediscovered and confirmed in the early 20th century cementing his status as the “father of modern genetics.”
Gregor Mendel
Gregor Mendel (1822–1884): Gregor Mendel was an Augustinian monk and botanist whose experiments in breeding garden peas led to the establishment of the fundamental laws of genetics. Born in the early 19th century in what is now the Czech Republic, Mendel’s meticulous work with pea plants laid the foundation for the field of genetics. He […] -

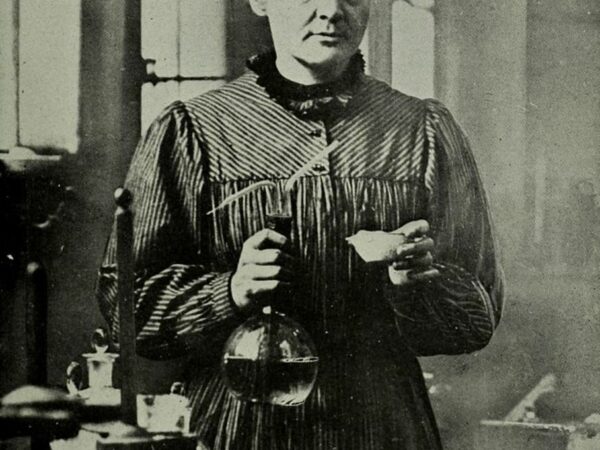
Marie Curie
Marie Curie (1867–1934)Marie Curie (1867–1934): Marie Curie was a revolutionary physicist and chemist who conducted research on radioactivity, a term she herself coined. Born in Poland, Curie’s extraordinary work led to the discovery of the radioactive elements polonium and radium. Her groundbreaking studies on radioactivity investigations into the spontaneous emission of radiation by certain substances contributed to the development of X-rays and cancer treatment. Curie was the first woman to win a Nobel Prize and she remains the only person to have won the prestigious award in two different scientific fields—Physics and Chemistry. Despite facing numerous professional obstacles because of her gender, Curie’s relentless dedication to scientific discovery left a legacy in both the scientific community.
Marie Curie
Marie Curie (1867–1934): Marie Curie was a revolutionary physicist and chemist who conducted research on radioactivity, a term she herself coined. Born in Poland, Curie’s extraordinary work led to the discovery of the radioactive elements polonium and radium. Her groundbreaking studies on radioactivity investigations into the spontaneous emission of radiation by certain substances contributed to […] -

Max Planck
Max Planck (1858–1947)Max Planck (1858–1947): Max Planck was a German theoretical physicist who made contributions to the understanding of atomic and subatomic processes. Born in the late 19th century, Planck is best known for originating quantum theory which reshaped our understanding of the atomic and subatomic world. His creative work began with an attempt to solve the black-body radiation problem. To reconcile experimental observations with theory, Planck proposed that energy was emitted in discrete units rather than in a continuous wave. This led to the formulation of Planck’s constant which is a central quantity in quantum mechanics. For his work on quantum theory, he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1918 which marked a significant departure from classical physics and brought in a new era in the field of theoretical physics.
Max Planck
Max Planck (1858–1947): Max Planck was a German theoretical physicist who made contributions to the understanding of atomic and subatomic processes. Born in the late 19th century, Planck is best known for originating quantum theory which reshaped our understanding of the atomic and subatomic world. His creative work began with an attempt to solve the […] -

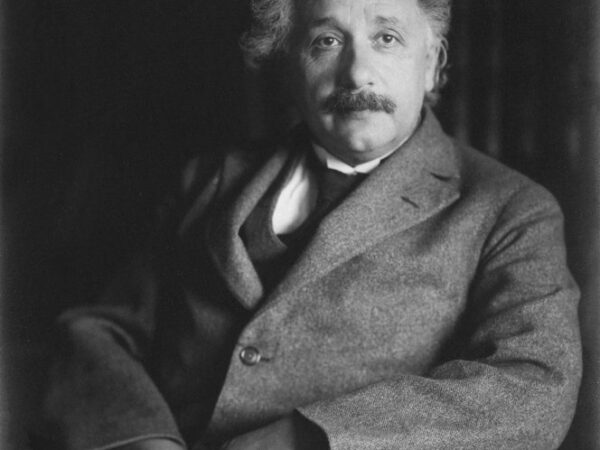
Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein (1879–1955)Albert Einstein (1879–1955): Albert Einstein was a German-born theoretical physicist who is perhaps the most well-known scientist of the 20th century. Einstein made advanced contributions to our understanding of the fundamental laws of the universe with his theory of relativity reshaping the fields of physics and cosmology. His special theory of relativity published in 1905, introduced the famous equation E=mc^2 which states that energy (E) is equivalent to mass (m) times the speed of light (c) squared. This equation has far-reaching implications including the explanation of the vast energies released in nuclear reactions. In 1915 Einstein presented his general theory of relativity which stated that gravity is not a force but a curvature of space-time caused by mass and energy. His predictions solidified his reputation as a revolutionary scientific thinker. Einstein was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1921 for his explanation of the photoelectric effect which also laid the groundwork for the development of quantum mechanics.
Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein (1879–1955): Albert Einstein was a German-born theoretical physicist who is perhaps the most well-known scientist of the 20th century. Einstein made advanced contributions to our understanding of the fundamental laws of the universe with his theory of relativity reshaping the fields of physics and cosmology. His special theory of relativity published in 1905, […] -

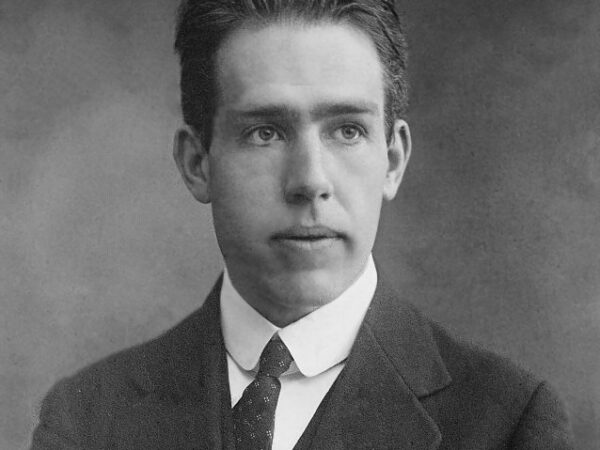
Niels Bohr
Niels Bohr (1885–1962)Niels Bohr (1885–1962): Niels Bohr was a Danish physicist who made significant contributions to the understanding of atomic structure and the early development of quantum mechanics. Born in the late 19th century, Bohr introduced the concept that an atom is a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by orbiting electrons that exist in discrete energy levels. His innovative model of the atom known as the Bohr Model, suggest that electrons move in designated orbits around the nucleus and that the chemical properties of an element are largely determined by the number of electrons in the outer orbits. Bohr was also instrumental in developing the principle of complementarity which states that a quantum system can be understood in multiple, mutually exclusive, yet equally valid ways. Awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1922 for his work on atomic structures, Bohr’s work laid a crucial foundation for modern atomic physics.
Niels Bohr
Niels Bohr (1885–1962): Niels Bohr was a Danish physicist who made significant contributions to the understanding of atomic structure and the early development of quantum mechanics. Born in the late 19th century, Bohr introduced the concept that an atom is a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by orbiting electrons that exist in discrete energy levels. […] -

Ernest O. Lawrence
Ernest O. Lawrence (1901–1958)Ernest O. Lawrence (1901–1958): Ernest O. Lawrence was an American physicist and winner of the Nobel Prize in Phyics in 1939. Best known for inventing the cyclotron, a type of particle accelerator that became a vital tool in both physics and nuclear medicine. Born in the early 20th century, Lawrence’s cyclotron used a strong magnetic field to accelerate charged particles along a spiral path achieving energies sufficient to dislodge protons or neutrons from the nucleus of an atom. This marked an advancement in the field of nuclear physics which opened the door for explorations into the structure of the atomic nucleus and leading to the discovery of many new isotopes. In the field of medicine, the cyclotron’s ability to produce radioactive isotopes was critical for both diagnostic procedures and treatment particularly in cancer therapy.
Ernest O. Lawrence
Ernest O. Lawrence (1901–1958): Ernest O. Lawrence was an American physicist and winner of the Nobel Prize in Phyics in 1939. Best known for inventing the cyclotron, a type of particle accelerator that became a vital tool in both physics and nuclear medicine. Born in the early 20th century, Lawrence's cyclotron used a strong magnetic field to accelerate charged particles along a spiral path achieving energies sufficient to dislodge protons or neutrons from the nucleus of an atom. This marked an advancement in the field of nuclear physics which opened the door for explorations into the structure of the atomic nucleus and leading to the discovery of many new isotopes. In the field of medicine, the cyclotron's ability to produce radioactive isotopes was critical for both diagnostic procedures and treatment particularly in cancer therapy. -

Erwin Schrödinger
Erwin Schrödinger (1887–1961)Erwin Schrödinger (1887–1961): Erwin Schrödinger was an Austrian-Irish physicist who made radical contributions to the wave theory of matter and the field of quantum mechanics. Born in the late 19th century, Schrödinger is most recognized for his wave equation now known as the Schrödinger equation. This equation describes how the quantum state of a quantum system changes over time. It’s a foundational standard of quantum mechanics providing detailed predictions of the behavior of particles at the quantum level. Beyond his wave equation, Schrödinger is also known for his philosophical “Schrödinger’s cat” thought experiment which poses intriguing questions about the nature of quantum states. Awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1933 for his work on quantum mechanics, Schrödinger’s theories continue to influence modern physics, chemistry, and other fields of science.
Erwin Schrödinger
Erwin Schrödinger (1887–1961): Erwin Schrödinger was an Austrian-Irish physicist who made radical contributions to the wave theory of matter and the field of quantum mechanics. Born in the late 19th century, Schrödinger is most recognized for his wave equation now known as the Schrödinger equation. This equation describes how the quantum state of a quantum […] -

Linus Pauling
Linus Pauling (1901–1994)Linus Pauling (1901–1994): Linus Pauling was an American chemist and peace activist who made profound contributions to the fields of quantum chemistry and biochemistry. Born in the early 20th century, Pauling’s work in molecular structure and bonding led to many breakthroughs in both theoretical and applied chemistry. He developed the concept of electronegativity and valence bond theory, crucial elements in the study of chemical bonding. His exploration into the nature of the chemical bond helped establish the field of molecular biology. His model of the alpha-helix and beta-sheet significantly impacted the study of biochemistry. Pauling was awarded two Nobel Prizes in Chemistry in 1954 for his work on the nature of the chemical bond and in 1962 for his efforts in advocating against nuclear weapons testing.
Linus Pauling
Linus Pauling (1901–1994): Linus Pauling was an American chemist and peace activist who made profound contributions to the fields of quantum chemistry and biochemistry. Born in the early 20th century, Pauling’s work in molecular structure and bonding led to many breakthroughs in both theoretical and applied chemistry. He developed the concept of electronegativity and valence […] -

Barbara McClintock
Barbara McClintock (1902–1992)Barbara McClintock (1902–1992): Barbara McClintock was an American geneticist and cytogeneticist who is best known for her discovery of transposons, or “jumping genes” – a radical find in the field of genetics. Born in the early 20th century, McClintock’s work predominantly focused on maize and through her studies she demonstrated that genes are responsible for turning physical characteristics on and off. One of her discovery was that of transposons, segments of DNA that can move around to different positions in the genome of a single cell. This changed the understanding of genetics, proving that genomes are not static but dynamic and adaptable entities. McClintock was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1983 and remains the only woman to receive an unshared Nobel Prize in that category.
Barbara McClintock
Barbara McClintock (1902–1992): Barbara McClintock was an American geneticist and cytogeneticist who is best known for her discovery of transposons, or “jumping genes” – a radical find in the field of genetics. Born in the early 20th century, McClintock’s work predominantly focused on maize and through her studies she demonstrated that genes are responsible for […] -

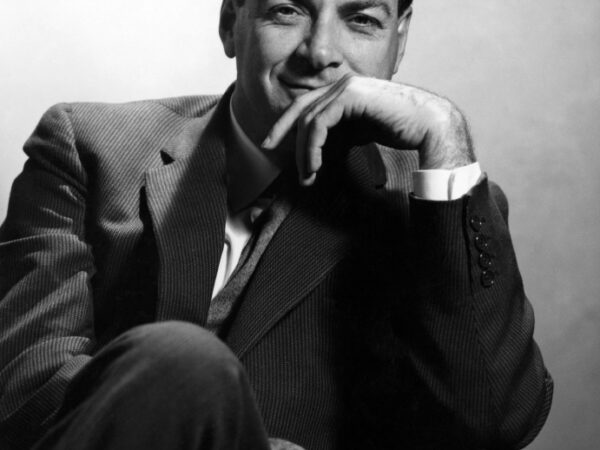
Richard Feynman
Richard Feynman (1918–1988)Richard Feynman (1918–1988): Richard Feynman was an American theoretical physicist known for his significant contributions to quantum mechanics and particle physics. Born in the early 20th century, Feynman is celebrated for his path integral formulation of quantum mechanics, a method to calculate quantum behavior by considering every possible path a particle can take. This approach provided new insights into the behavior of particles at the quantum level and was influential in the development of quantum field theory. Feynman is known for his Feynman diagrams, a graphic representation tool used extensively in particle physics to pictorially encode the mathematical expressions describing the behavior of subatomic particles. Awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1965 for his contributions to the development of quantum electrodynamics, Feynman’s work continues to be model for theoretical physics.
Richard Feynman
Richard Feynman (1918–1988): Richard Feynman was an American theoretical physicist known for his significant contributions to quantum mechanics and particle physics. Born in the early 20th century, Feynman is celebrated for his path integral formulation of quantum mechanics, a method to calculate quantum behavior by considering every possible path a particle can take. This approach […] -
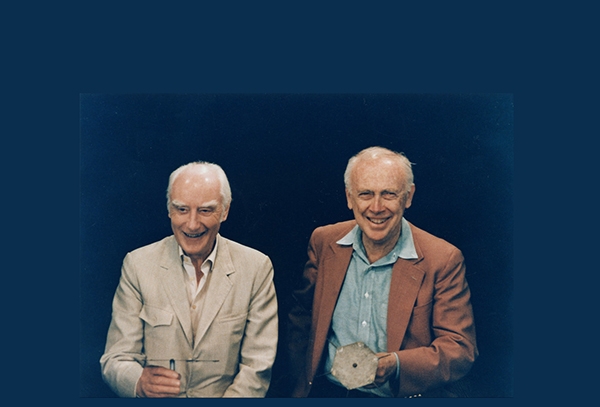

James Watson and Francis Crick
Watson and Crick (1916–2004)James Watson (born 1928) and Francis Crick (1916–2004): James Watson and Francis Crick were a pair of scientists who together proposed the double helix structure of the DNA molecule, an important discovery in the field of biology. Watson, an American molecular biologist, and Crick, a British biophysicist, began their collaboration at the University of Cambridge in the early 1950s. Building upon the work of others they constructed a model of DNA as a double helix, with pairs of nucleotides forming the “rungs” and sugar-phosphate molecules forming the “sides” of a twisted ladder. This discovery published in 1953 revolutionized the understanding of heredity and paved the way for modern molecular biology. In 1962, Watson and Crick were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine for their groundbreaking work on the structure of nucleic acids.
James Watson and Francis Crick
James Watson (born 1928) and Francis Crick (1916–2004): James Watson and Francis Crick were a pair of scientists who together proposed the double helix structure of the DNA molecule, an important discovery in the field of biology. Watson, an American molecular biologist, and Crick, a British biophysicist, began their collaboration at the University of Cambridge […] -

Rosalind Franklin
Rosalind Franklin (1920–1958)Rosalind Franklin (1920–1958): Rosalind Franklin was a British chemist and X-ray crystallographer whose contributions to the understanding of molecular structures helped unravel the structure of DNA. Born in the early 20th century, Franklin worked at King’s College London where she used X-ray diffraction techniques to examine the structure of DNA. Her photographs provided key insights into the molecule’s double helix structure. Franklin’s contributions were not fully recognized during her lifetime. Beyond DNA, she made significant contributions to the understanding of the molecular structures of RNA, viruses, coal, and graphite. Although she passed away before the Nobel Prize was awarded for the discovery of the structure of DNA, her work continues to be recognized for its impact on the fields of biology and chemistry.
Rosalind Franklin
Rosalind Franklin (1920–1958): Rosalind Franklin was a British chemist and X-ray crystallographer whose contributions to the understanding of molecular structures helped unravel the structure of DNA. Born in the early 20th century, Franklin worked at King’s College London where she used X-ray diffraction techniques to examine the structure of DNA. Her photographs provided key insights […] -

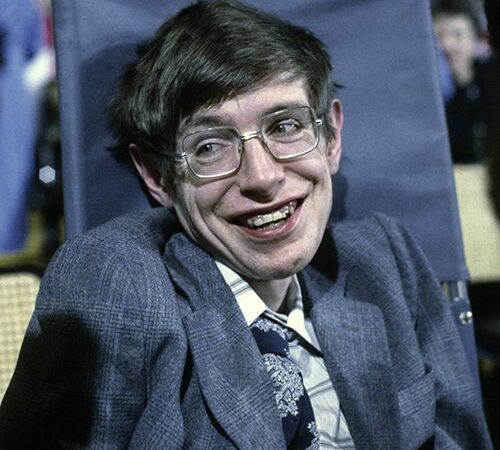
Stephen Hawking
Stephen Hawking (1942–2018)Stephen Hawking (1942–2018): Stephen Hawking was a British theoretical physicist and cosmologist, best known for his contributions to the fields of cosmology, general relativity, and quantum gravity. Born in the mid-20th century, Hawking’s work centered around the physics of black holes and the universe. He proposed that black holes are not completely black but emit radiation due to quantum effects near the event horizon. This discovery was advanced as it combined principles from quantum mechanics and general relativity. Hawking also applied the mathematics of black holes to the entire universe resulting in our current understanding of the Big Bang and the eventual fate of the universe. Despite battling a rare form of motor neurone disease that left him almost entirely paralyzed, Hawking continued his research and writing becoming a symbol of the power of the human mind.
Stephen Hawking
Stephen Hawking (1942–2018): Stephen Hawking was a British theoretical physicist and cosmologist, best known for his contributions to the fields of cosmology, general relativity, and quantum gravity. Born in the mid-20th century, Hawking’s work centered around the physics of black holes and the universe. He proposed that black holes are not completely black but emit […] -

Tim Berners-Lee
Tim Berners-Lee (born 1955)Tim Berners-Lee (born 1955): Tim Berners-Lee is a British computer scientist recognized globally as the inventor of the World Wide Web. Born in the mid-20th century, Berners-Lee envisioned a unifying structure for linking information across different computers. In 1989 while working at CERN, he proposed a decentralized system of information management. This led to the first successful communication between a Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) client and server via the internet in late 1990. Berners-Lee’s invention of the World Wide Web which included the establishment of HTTP, Uniform Resource Locators (URLs), and HTML, changed the way we create and consume information. Today, it underpins the modern digital age, profoundly shaping many facets of society, including communication, education, business, and entertainment.
Tim Berners-Lee
Tim Berners-Lee (born 1955): Tim Berners-Lee is a British computer scientist recognized globally as the inventor of the World Wide Web. Born in the mid-20th century, Berners-Lee envisioned a unifying structure for linking information across different computers. In 1989 while working at CERN, he proposed a decentralized system of information management. This led to the […]
- Aristotle (384–322 BC)
- Archimedes (c. 287–212 BC)
- Alhazen (965–1040)
- Copernicus (1473–1543)
- Galileo (1564–1642)
- Johannes Kepler (1571–1630)
- Isaac Newton (1643–1727)
- Carl Linnaeus (1707–1778)
- Antoine Lavoisier (1743–1794)
- Michael Faraday (1791–1867)
- Charles Darwin (1809–1882)
- Gregor Mendel (1822–1884)
- Marie Curie (1867–1934)
- Max Planck (1858–1947)
- Albert Einstein (1879–1955)
- Niels Bohr (1885–1962)
- Ernest O. Lawrence (1901–1958)
- Erwin Schrödinger (1887–1961)
- Linus Pauling (1901–1994)
- Barbara McClintock (1902–1992)
- Richard Feynman (1918–1988)
- Watson and Crick (1916–2004)
- Rosalind Franklin (1920–1958)
- Stephen Hawking (1942–2018)
- Tim Berners-Lee (born 1955)
-

Aristotle
Aristotle (384–322 BC)Aristotle (384–322 BC): Aristotle was a leading figure in the history of ancient philosophy and science. Born in Northern Greece, he was a philosopher and genius during the Classical period. As a student of Plato and the teacher of Alexander the Great, he was part of an intellectual lineage that profoundly influenced the Western intellectual tradition. Aristotle’s impact on philosophy and various sciences cannot be overstated. His inquiries spanned a multitude of subjects, including physics, biology, zoology, metaphysics, logic, ethics, aesthetics, poetry, theater, music, rhetoric, psychology, and politics. In the realm of physical science, his meticulous observations and powerful theorizations formed the basis for subsequent scientific exploration.
Aristotle
Aristotle (384–322 BC): Aristotle was a leading figure in the history of ancient philosophy and science. Born in Northern Greece, he was a philosopher and genius during the Classical period. As a student of Plato and the teacher of Alexander the Great, he was part of an intellectual lineage that profoundly influenced the Western intellectual […] -

Archimedes
Archimedes (c. 287–212 BC)Archimedes (c. 287–212 BC): Archimedes was an Ancient Greek mathematician, physicist, engineer, inventor, and astronomer whose contributions were significant in the development of the foundations of mathematics and science. His vast intellect and knack for problem-solving made him one of the most influential figures in the scientific world. Archimedes formulated concepts including the principles of leverage and buoyancy which are still widely used in modern physics and engineering. He also invented practical devices including the screw pump that bears his name – the Archimedean screw. Archimedes also made advancements in the field of mathematics with the estimate of pi and the method of exhaustion which is a precursor to integral calculus.
Archimedes
Archimedes (c. 287–212 BC): Archimedes was an Ancient Greek mathematician, physicist, engineer, inventor, and astronomer whose contributions were significant in the development of the foundations of mathematics and science. His vast intellect and knack for problem-solving made him one of the most influential figures in the scientific world. Archimedes formulated concepts including the principles of […] -

Alhazen
Alhazen (965–1040)Alhazen (Ibn al-Haytham) (965–1040): Alhazen was a renowned Arab mathematician, astronomer, and physicist, known for his contributions to the principles of optics and visual perception. His work in the field of optics shifted the understanding of light and vision. He is considered the father of modern optics. Alhazen introduced the concept of analyzing light through the use of a pinhole camera and was also the first to understand that vision occurs when light bounces off an object and then is directed to one’s eyes. Alhazen’s meticulous approach to understanding and explaining scientific phenomena using observation, hypothesis, and experimental verification laid the groundwork for the modern scientific method.
Alhazen
Alhazen (Ibn al-Haytham) (965–1040): Alhazen was a renowned Arab mathematician, astronomer, and physicist, known for his contributions to the principles of optics and visual perception. His work in the field of optics shifted the understanding of light and vision. He is considered the father of modern optics. Alhazen introduced the concept of analyzing light through […] -

Copernicus
Copernicus (1473–1543)Nicolaus Copernicus (1473–1543): Nicolaus Copernicus revolutionized our understanding of the cosmos. Known primarily for formulating a heliocentric cosmology, Copernicus’ model displaced the Earth from the center of the universe and positioned the Sun at the heart of the solar system. Although controversial in his time, this perspective provided the foundation for the future development of modern astronomy, changing the course of scientific thought forever.
Copernicus
Nicolaus Copernicus (1473–1543): Nicolaus Copernicus revolutionized our understanding of the cosmos. Known primarily for formulating a heliocentric cosmology, Copernicus’ model displaced the Earth from the center of the universe and positioned the Sun at the heart of the solar system. Although controversial in his time, this perspective provided the foundation for the future development of […] -

Galileo
Galileo (1564–1642)Galileo Galilei (1564–1642): Galileo is often regarded as the “father of observational astronomy,” and was a important figure in the Scientific Revolution. He made significant improvements to the telescope and subsequently made critical astronomical observations that supported Copernican concepts. Galileo’s observations of inertia and the laws of motion laid the groundwork for the principles of classical physics. Galileo’s work spanned a variety of fields, including physics, engineering, and natural philosophy, and his contributions have had a foundational impact on the trajectory of scientific discovery.
Galileo
Galileo Galilei (1564–1642): Galileo is often regarded as the “father of observational astronomy,” and was a important figure in the Scientific Revolution. He made significant improvements to the telescope and subsequently made critical astronomical observations that supported Copernican concepts. Galileo’s observations of inertia and the laws of motion laid the groundwork for the principles of […] -

Johannes Kepler
Johannes Kepler (1571–1630)Johannes Kepler (1571–1630): Johannes Kepler was a German astronomer, mathematician, and astrologer whose innovative work transformed our understanding of the cosmos. Kepler formulated three major laws of planetary motion which corrected and refined the previous heliocentric model proposed by Nicolaus Copernicus. His laws accurately described the elliptical orbits of planets around the sun and the relationship between a planet’s orbital speed and its distance from the sun. Giving us the precise correlation between the orbital periods of any two planets. These laws provided a powerful model for planetary motion and formed a vital link in the chain of scientific understanding that led to the formulation of Newton’s law of universal gravitation.
Johannes Kepler
Johannes Kepler (1571–1630): Johannes Kepler was a German astronomer, mathematician, and astrologer whose innovative work transformed our understanding of the cosmos. Kepler formulated three major laws of planetary motion which corrected and refined the previous heliocentric model proposed by Nicolaus Copernicus. His laws accurately described the elliptical orbits of planets around the sun and the […] -

Isaac Newton
Isaac Newton (1643–1727)Isaac Newton (1643–1727): Isaac Newton was a significant figure in the scientific revolution of the 17th century. Born in England, he was a mathematician, physicist, and astronomer who is best known for formulating the laws of motion and universal gravitation. Newton’s three laws of motion describe the relationship between a body and the forces acting upon it and its motion in response to those forces. These laws laid the groundwork for classical mechanics. The law of universal gravitation described the fundamental force of attraction that exists between any two masses. His ideas continue to influence our understanding of the physical universe. Newton’s insights marked a new era in scientific theory while shifting the course of physics from a descriptive to a predictive discipline.
Isaac Newton
Isaac Newton (1643–1727): Isaac Newton was a significant figure in the scientific revolution of the 17th century. Born in England, he was a mathematician, physicist, and astronomer who is best known for formulating the laws of motion and universal gravitation. Newton’s three laws of motion describe the relationship between a body and the forces acting […] -

Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (1707–1778)Carl Linnaeus (1707–1778): Carl Linnaeus was a Swedish botanist, physician, and zoologist who established the modern system of naming organisms known as binomial nomenclature. Born in the early 18th century, Linnaeus is often referred to as the “father of modern taxonomy” for his contributions to the field. He developed a system for classifying and naming species based on shared characteristics. This method that is still in use today. His ordered system of classification in which species are grouped into broader categories of genus, family, order, class, phylum, and kingdom, provided an essential framework for the study of biology.
Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (1707–1778): Carl Linnaeus was a Swedish botanist, physician, and zoologist who established the modern system of naming organisms known as binomial nomenclature. Born in the early 18th century, Linnaeus is often referred to as the “father of modern taxonomy” for his contributions to the field. He developed a system for classifying and naming […] -

Antoine Lavoisier
Antoine Lavoisier (1743–1794)Antoine Lavoisier (1743–1794): Antoine Lavoisier was a prominent French chemist renowned for his significant contributions that reshaped the field of chemistry in the late 18th century. He developed the theory of conservation of mass which states that the mass of a closed system will remain constant regardless of the processes acting inside the system. This revolutionary concept led to the law of conservation of matter in chemical reactions. Lavoisier also identified and named two fundamental chemical elements: oxygen and hydrogen. His experiments led him to propose that combustion and respiration are caused by chemical reactions with oxygen, effectively debunking the long-standing phlogiston theory. Due to his work, Lavoisier is often referred to as the “father of modern chemistry.” His rigorous methods, insistence on precise measurement and clear definitions significantly elevated the scientific approach in chemistry.
Antoine Lavoisier
Antoine Lavoisier (1743–1794): Antoine Lavoisier was a prominent French chemist renowned for his significant contributions that reshaped the field of chemistry in the late 18th century. He developed the theory of conservation of mass which states that the mass of a closed system will remain constant regardless of the processes acting inside the system. This […] -

Michael Faraday
Michael Faraday (1791–1867)Michael Faraday (1791–1867): Michael Faraday was a British scientist known for his significant contributions to the fields of electromagnetism and electrochemistry. Born to a poor family in the late 18th century, Faraday received minimal education but his scientific curiosity led him to become one of the most influential scientists in history. His main discoveries include the principles of electromagnetic induction, diamagnetism, and electrolysis. Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction, which states that a change in the magnetic field within a closed loop of wire induces an electromotive force in the wire, is a fundamental principle used in modern electric power generation and transmission. His work on diamagnetism was a pioneering endeavor in the field. His laws of electrolysis serve as the basis for electrochemistry, which has numerous applications in batteries and fuel cells. Faraday’s contributions have had enduring impact on our technological world, including electric motor technology and telecommunications.
Michael Faraday
Michael Faraday (1791–1867): Michael Faraday was a British scientist known for his significant contributions to the fields of electromagnetism and electrochemistry. Born to a poor family in the late 18th century, Faraday received minimal education but his scientific curiosity led him to become one of the most influential scientists in history. His main discoveries include […] -

Charles Darwin
Charles Darwin (1809–1882)Charles Darwin (1809–1882): Charles Darwin was a renowned British naturalist and biologist who fundamentally changed the way we understand the natural world. Born in the early 19th century, Darwin formulated the theory of natural selection, a revolutionary concept that explains how species evolve over time through gradual changes. Darwin argued that individuals within a species show variation in their traits and those with traits better suited to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce. Over generations, these important traits become more common within the population leading to evolutionary change. This idea was presented in his book, “On the Origin of Species,” which shook the scientific world and caused a paradigm shift in our understanding of life on Earth. Darwin laid the groundwork for the modern science of biology, making him one of the most influential figures in human history.
Charles Darwin
Charles Darwin (1809–1882): Charles Darwin was a renowned British naturalist and biologist who fundamentally changed the way we understand the natural world. Born in the early 19th century, Darwin formulated the theory of natural selection, a revolutionary concept that explains how species evolve over time through gradual changes. Darwin argued that individuals within a species […] -

Gregor Mendel
Gregor Mendel (1822–1884)Gregor Mendel (1822–1884): Gregor Mendel was an Augustinian monk and botanist whose experiments in breeding garden peas led to the establishment of the fundamental laws of genetics. Born in the early 19th century in what is now the Czech Republic, Mendel’s meticulous work with pea plants laid the foundation for the field of genetics. He demonstrated that the inheritance of certain traits in the plants follows particular patterns now referred to as the laws of Mendelian inheritance. His most significant contributions include the Law of Segregation which states that an individual inherits one allele from each parent for each trait. His Law of Independent Assortment pose that traits are passed independently of one another from parents to offspring. Mendel’s work was largely unrecognized during his lifetime but was rediscovered and confirmed in the early 20th century cementing his status as the “father of modern genetics.”
Gregor Mendel
Gregor Mendel (1822–1884): Gregor Mendel was an Augustinian monk and botanist whose experiments in breeding garden peas led to the establishment of the fundamental laws of genetics. Born in the early 19th century in what is now the Czech Republic, Mendel’s meticulous work with pea plants laid the foundation for the field of genetics. He […] -

Marie Curie
Marie Curie (1867–1934)Marie Curie (1867–1934): Marie Curie was a revolutionary physicist and chemist who conducted research on radioactivity, a term she herself coined. Born in Poland, Curie’s extraordinary work led to the discovery of the radioactive elements polonium and radium. Her groundbreaking studies on radioactivity investigations into the spontaneous emission of radiation by certain substances contributed to the development of X-rays and cancer treatment. Curie was the first woman to win a Nobel Prize and she remains the only person to have won the prestigious award in two different scientific fields—Physics and Chemistry. Despite facing numerous professional obstacles because of her gender, Curie’s relentless dedication to scientific discovery left a legacy in both the scientific community.
Marie Curie
Marie Curie (1867–1934): Marie Curie was a revolutionary physicist and chemist who conducted research on radioactivity, a term she herself coined. Born in Poland, Curie’s extraordinary work led to the discovery of the radioactive elements polonium and radium. Her groundbreaking studies on radioactivity investigations into the spontaneous emission of radiation by certain substances contributed to […] -

Max Planck
Max Planck (1858–1947)Max Planck (1858–1947): Max Planck was a German theoretical physicist who made contributions to the understanding of atomic and subatomic processes. Born in the late 19th century, Planck is best known for originating quantum theory which reshaped our understanding of the atomic and subatomic world. His creative work began with an attempt to solve the black-body radiation problem. To reconcile experimental observations with theory, Planck proposed that energy was emitted in discrete units rather than in a continuous wave. This led to the formulation of Planck’s constant which is a central quantity in quantum mechanics. For his work on quantum theory, he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1918 which marked a significant departure from classical physics and brought in a new era in the field of theoretical physics.
Max Planck
Max Planck (1858–1947): Max Planck was a German theoretical physicist who made contributions to the understanding of atomic and subatomic processes. Born in the late 19th century, Planck is best known for originating quantum theory which reshaped our understanding of the atomic and subatomic world. His creative work began with an attempt to solve the […] -

Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein (1879–1955)Albert Einstein (1879–1955): Albert Einstein was a German-born theoretical physicist who is perhaps the most well-known scientist of the 20th century. Einstein made advanced contributions to our understanding of the fundamental laws of the universe with his theory of relativity reshaping the fields of physics and cosmology. His special theory of relativity published in 1905, introduced the famous equation E=mc^2 which states that energy (E) is equivalent to mass (m) times the speed of light (c) squared. This equation has far-reaching implications including the explanation of the vast energies released in nuclear reactions. In 1915 Einstein presented his general theory of relativity which stated that gravity is not a force but a curvature of space-time caused by mass and energy. His predictions solidified his reputation as a revolutionary scientific thinker. Einstein was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1921 for his explanation of the photoelectric effect which also laid the groundwork for the development of quantum mechanics.
Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein (1879–1955): Albert Einstein was a German-born theoretical physicist who is perhaps the most well-known scientist of the 20th century. Einstein made advanced contributions to our understanding of the fundamental laws of the universe with his theory of relativity reshaping the fields of physics and cosmology. His special theory of relativity published in 1905, […] -

Niels Bohr
Niels Bohr (1885–1962)Niels Bohr (1885–1962): Niels Bohr was a Danish physicist who made significant contributions to the understanding of atomic structure and the early development of quantum mechanics. Born in the late 19th century, Bohr introduced the concept that an atom is a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by orbiting electrons that exist in discrete energy levels. His innovative model of the atom known as the Bohr Model, suggest that electrons move in designated orbits around the nucleus and that the chemical properties of an element are largely determined by the number of electrons in the outer orbits. Bohr was also instrumental in developing the principle of complementarity which states that a quantum system can be understood in multiple, mutually exclusive, yet equally valid ways. Awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1922 for his work on atomic structures, Bohr’s work laid a crucial foundation for modern atomic physics.
Niels Bohr
Niels Bohr (1885–1962): Niels Bohr was a Danish physicist who made significant contributions to the understanding of atomic structure and the early development of quantum mechanics. Born in the late 19th century, Bohr introduced the concept that an atom is a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by orbiting electrons that exist in discrete energy levels. […] -

Ernest O. Lawrence
Ernest O. Lawrence (1901–1958)Ernest O. Lawrence (1901–1958): Ernest O. Lawrence was an American physicist and winner of the Nobel Prize in Phyics in 1939. Best known for inventing the cyclotron, a type of particle accelerator that became a vital tool in both physics and nuclear medicine. Born in the early 20th century, Lawrence’s cyclotron used a strong magnetic field to accelerate charged particles along a spiral path achieving energies sufficient to dislodge protons or neutrons from the nucleus of an atom. This marked an advancement in the field of nuclear physics which opened the door for explorations into the structure of the atomic nucleus and leading to the discovery of many new isotopes. In the field of medicine, the cyclotron’s ability to produce radioactive isotopes was critical for both diagnostic procedures and treatment particularly in cancer therapy.
Ernest O. Lawrence
Ernest O. Lawrence (1901–1958): Ernest O. Lawrence was an American physicist and winner of the Nobel Prize in Phyics in 1939. Best known for inventing the cyclotron, a type of particle accelerator that became a vital tool in both physics and nuclear medicine. Born in the early 20th century, Lawrence's cyclotron used a strong magnetic field to accelerate charged particles along a spiral path achieving energies sufficient to dislodge protons or neutrons from the nucleus of an atom. This marked an advancement in the field of nuclear physics which opened the door for explorations into the structure of the atomic nucleus and leading to the discovery of many new isotopes. In the field of medicine, the cyclotron's ability to produce radioactive isotopes was critical for both diagnostic procedures and treatment particularly in cancer therapy. -

Erwin Schrödinger
Erwin Schrödinger (1887–1961)Erwin Schrödinger (1887–1961): Erwin Schrödinger was an Austrian-Irish physicist who made radical contributions to the wave theory of matter and the field of quantum mechanics. Born in the late 19th century, Schrödinger is most recognized for his wave equation now known as the Schrödinger equation. This equation describes how the quantum state of a quantum system changes over time. It’s a foundational standard of quantum mechanics providing detailed predictions of the behavior of particles at the quantum level. Beyond his wave equation, Schrödinger is also known for his philosophical “Schrödinger’s cat” thought experiment which poses intriguing questions about the nature of quantum states. Awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1933 for his work on quantum mechanics, Schrödinger’s theories continue to influence modern physics, chemistry, and other fields of science.
Erwin Schrödinger
Erwin Schrödinger (1887–1961): Erwin Schrödinger was an Austrian-Irish physicist who made radical contributions to the wave theory of matter and the field of quantum mechanics. Born in the late 19th century, Schrödinger is most recognized for his wave equation now known as the Schrödinger equation. This equation describes how the quantum state of a quantum […] -

Linus Pauling
Linus Pauling (1901–1994)Linus Pauling (1901–1994): Linus Pauling was an American chemist and peace activist who made profound contributions to the fields of quantum chemistry and biochemistry. Born in the early 20th century, Pauling’s work in molecular structure and bonding led to many breakthroughs in both theoretical and applied chemistry. He developed the concept of electronegativity and valence bond theory, crucial elements in the study of chemical bonding. His exploration into the nature of the chemical bond helped establish the field of molecular biology. His model of the alpha-helix and beta-sheet significantly impacted the study of biochemistry. Pauling was awarded two Nobel Prizes in Chemistry in 1954 for his work on the nature of the chemical bond and in 1962 for his efforts in advocating against nuclear weapons testing.
Linus Pauling
Linus Pauling (1901–1994): Linus Pauling was an American chemist and peace activist who made profound contributions to the fields of quantum chemistry and biochemistry. Born in the early 20th century, Pauling’s work in molecular structure and bonding led to many breakthroughs in both theoretical and applied chemistry. He developed the concept of electronegativity and valence […] -

Barbara McClintock
Barbara McClintock (1902–1992)Barbara McClintock (1902–1992): Barbara McClintock was an American geneticist and cytogeneticist who is best known for her discovery of transposons, or “jumping genes” – a radical find in the field of genetics. Born in the early 20th century, McClintock’s work predominantly focused on maize and through her studies she demonstrated that genes are responsible for turning physical characteristics on and off. One of her discovery was that of transposons, segments of DNA that can move around to different positions in the genome of a single cell. This changed the understanding of genetics, proving that genomes are not static but dynamic and adaptable entities. McClintock was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1983 and remains the only woman to receive an unshared Nobel Prize in that category.
Barbara McClintock
Barbara McClintock (1902–1992): Barbara McClintock was an American geneticist and cytogeneticist who is best known for her discovery of transposons, or “jumping genes” – a radical find in the field of genetics. Born in the early 20th century, McClintock’s work predominantly focused on maize and through her studies she demonstrated that genes are responsible for […] -

Richard Feynman
Richard Feynman (1918–1988)Richard Feynman (1918–1988): Richard Feynman was an American theoretical physicist known for his significant contributions to quantum mechanics and particle physics. Born in the early 20th century, Feynman is celebrated for his path integral formulation of quantum mechanics, a method to calculate quantum behavior by considering every possible path a particle can take. This approach provided new insights into the behavior of particles at the quantum level and was influential in the development of quantum field theory. Feynman is known for his Feynman diagrams, a graphic representation tool used extensively in particle physics to pictorially encode the mathematical expressions describing the behavior of subatomic particles. Awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1965 for his contributions to the development of quantum electrodynamics, Feynman’s work continues to be model for theoretical physics.
Richard Feynman
Richard Feynman (1918–1988): Richard Feynman was an American theoretical physicist known for his significant contributions to quantum mechanics and particle physics. Born in the early 20th century, Feynman is celebrated for his path integral formulation of quantum mechanics, a method to calculate quantum behavior by considering every possible path a particle can take. This approach […] -

James Watson and Francis Crick
Watson and Crick (1916–2004)James Watson (born 1928) and Francis Crick (1916–2004): James Watson and Francis Crick were a pair of scientists who together proposed the double helix structure of the DNA molecule, an important discovery in the field of biology. Watson, an American molecular biologist, and Crick, a British biophysicist, began their collaboration at the University of Cambridge in the early 1950s. Building upon the work of others they constructed a model of DNA as a double helix, with pairs of nucleotides forming the “rungs” and sugar-phosphate molecules forming the “sides” of a twisted ladder. This discovery published in 1953 revolutionized the understanding of heredity and paved the way for modern molecular biology. In 1962, Watson and Crick were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine for their groundbreaking work on the structure of nucleic acids.
James Watson and Francis Crick
James Watson (born 1928) and Francis Crick (1916–2004): James Watson and Francis Crick were a pair of scientists who together proposed the double helix structure of the DNA molecule, an important discovery in the field of biology. Watson, an American molecular biologist, and Crick, a British biophysicist, began their collaboration at the University of Cambridge […] -

Rosalind Franklin
Rosalind Franklin (1920–1958)Rosalind Franklin (1920–1958): Rosalind Franklin was a British chemist and X-ray crystallographer whose contributions to the understanding of molecular structures helped unravel the structure of DNA. Born in the early 20th century, Franklin worked at King’s College London where she used X-ray diffraction techniques to examine the structure of DNA. Her photographs provided key insights into the molecule’s double helix structure. Franklin’s contributions were not fully recognized during her lifetime. Beyond DNA, she made significant contributions to the understanding of the molecular structures of RNA, viruses, coal, and graphite. Although she passed away before the Nobel Prize was awarded for the discovery of the structure of DNA, her work continues to be recognized for its impact on the fields of biology and chemistry.
Rosalind Franklin
Rosalind Franklin (1920–1958): Rosalind Franklin was a British chemist and X-ray crystallographer whose contributions to the understanding of molecular structures helped unravel the structure of DNA. Born in the early 20th century, Franklin worked at King’s College London where she used X-ray diffraction techniques to examine the structure of DNA. Her photographs provided key insights […] -

Stephen Hawking
Stephen Hawking (1942–2018)Stephen Hawking (1942–2018): Stephen Hawking was a British theoretical physicist and cosmologist, best known for his contributions to the fields of cosmology, general relativity, and quantum gravity. Born in the mid-20th century, Hawking’s work centered around the physics of black holes and the universe. He proposed that black holes are not completely black but emit radiation due to quantum effects near the event horizon. This discovery was advanced as it combined principles from quantum mechanics and general relativity. Hawking also applied the mathematics of black holes to the entire universe resulting in our current understanding of the Big Bang and the eventual fate of the universe. Despite battling a rare form of motor neurone disease that left him almost entirely paralyzed, Hawking continued his research and writing becoming a symbol of the power of the human mind.
Stephen Hawking
Stephen Hawking (1942–2018): Stephen Hawking was a British theoretical physicist and cosmologist, best known for his contributions to the fields of cosmology, general relativity, and quantum gravity. Born in the mid-20th century, Hawking’s work centered around the physics of black holes and the universe. He proposed that black holes are not completely black but emit […] -

Tim Berners-Lee
Tim Berners-Lee (born 1955)Tim Berners-Lee (born 1955): Tim Berners-Lee is a British computer scientist recognized globally as the inventor of the World Wide Web. Born in the mid-20th century, Berners-Lee envisioned a unifying structure for linking information across different computers. In 1989 while working at CERN, he proposed a decentralized system of information management. This led to the first successful communication between a Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) client and server via the internet in late 1990. Berners-Lee’s invention of the World Wide Web which included the establishment of HTTP, Uniform Resource Locators (URLs), and HTML, changed the way we create and consume information. Today, it underpins the modern digital age, profoundly shaping many facets of society, including communication, education, business, and entertainment.
Tim Berners-Lee
Tim Berners-Lee (born 1955): Tim Berners-Lee is a British computer scientist recognized globally as the inventor of the World Wide Web. Born in the mid-20th century, Berners-Lee envisioned a unifying structure for linking information across different computers. In 1989 while working at CERN, he proposed a decentralized system of information management. This led to the […]
Technology & Engineering
Biology & Genetics
Interdisciplinary Studies
University Research